CACTUS MLC-240S Industrial Series M.2 SSD

Features
- Solid state design with no moving parts
- Capacities from 8GB to 256GB
- Available in M.2 2242, 2260 and 2280 form factors
- Compliant with Serial ATA 3.1 specifications
- Compliant with PCI Express M.2 specification, ver.1.0
- ATA-8 ACS2 compatible
- Supports Serial ATA Generation I/II/III transfer rate of 1.5/3.0/6.0 Gbps
- Supports ATA SMART Feature Set
- Supports ATA Security Feature Set
- Supports Data Set Management (TRIM)
- Supports NCQ w/ max. queue depth of 32
- Supports AHCI
- ECC capable of correcting up to 66 bit errors per 1KB
- Enhanced error correction, < 1 error in 1014 bits read
- Voltage support: 3.3V±5%
Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SATA SSD is a high capacity solid-state flash memory product that complies with the Serial ATA 3.1 standard and PCI Express M.2 1.0 standard and is functionally compatible with a SATA hard disk drive. Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD provides up to 256GB of formatted storage capacity.
Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD product uses high quality Industrial Grade MLC NAND flash memory from Kioxia Corporation. In addition, it includes an on-drive intelligent controller that manages interface protocols, data storage and retrieval as well as ECC, defect handling and diagnostics, power management, and clock control. The controller’s firmware is upgradeable, thus allowing feature enhancements and firmware updates while keeping the BOM stable
Supported Standards
Cactus Technologies® M.2 SSD is fully compatible with the following specification:
- ATA 8/ACS2 Specification published by ANSI
- Serial ATA 3.1 Specification published by the Serial ATA International Organization
- PCI Express M.2 Specification 1.0 published by PCI SIG
Product Features
Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD contains a high level, intelligent controller. This intelligent controller provides many capabilities including the following:
- Standard ATA register and command set (same as found on most magnetic disk drives).
- Manages details of erasing and programming flash memory independent of the host system
- Sophisticated defect managing capabilities (similar to magnetic disk drives).
- Sophisticated system for error recovery using powerful error correction code (ECC).
- Intelligent power management for low power operation.
Host and Technology Independence
Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD appears as a standard SATA disk drive to the host system. The drive utilizes a 512-byte sector which is the same as that in an IDE magnetic disk drive. To write or read a sector (or multiple sectors), the host computer software simply issues an ATA Read or Write command to the drive as per the SATA protocol. The host software then waits for the command to complete. The host system does not get involved in the details of how the flash memory is erased, programmed or read as this is all managed by the built-in controller in the drive. Also, with the intelligent on-board controller, the host system software will not require changing as new flash memory evolves. Thus, systems that support the Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD products today will continue to work with future Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSDs built with new flash technology without having to update or change host software.
Defect and Error Management
Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD contains a sophisticated defect and error management system similar to those found in magnetic disk drives. The defect management is completely transparent to the host and does not consume any user data space. The soft error rate for Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD is much lower than that of magnetic disk drives. In the extremely rare case where a read error does occur, the drive has sophisticated ECC to recover the data.These defect and error management systems, coupled with the solid-state construction, give Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSDs unparalleled reliability.
Power Supply Requirements
Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD operates at a voltage range of 3.3 volts ± 5%.
Product Specifications
For all the following specifications, values are defined at ambient temperature and nominal supply voltage unless otherwise stated.
System Environmental Specifications
Table 2-1. Environmental Specifications
| Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD | ||
| Temperature | Operating: | 0° C to +70° C (Standard) -40° C to +85° C (Extended) |
| Humidity | Operating & NonOperating: | 8% to 95%, non-condensing |
| Vibration | Operating & NonOperating: | 20G, MIL-STD-883G Method 2005.2, Condition A |
| Shock | Operating & NonOperating: | 3,000 G, MIL-STD-883G Method 2002.4, Condition C |
| Altitude (relative to sea level) | Operating & NonOperating: | 100,000 feet maximum |
Note: Extended temp. version is temperature screened via burn-in testing
System Power Requirements
Table 2-2. Power Requirements
| Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD | |||||||
| DC Input Voltage (VCC) 100 mV max. ripple (p-p) | 3.3V ±5% | ||||||
| 2242 | |||||||
| Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD | |||||||
| 8GB | 16GB | 32GB | 64GB | 128GB | 256GB | ||
| (Maximum Average Value) See Notes. | Idle: Reading: Writing: | 90 mA 260 mA 250 mA | 105mA 325mA 300mA | 100mA 330mA 310mA | 100mA 360mA 390mA | 105mA 430mA 555mA | 105mA 500mA 870mA |
| 2260/2280 | |||||||
| 8GB | 16GB | 32GB | 64GB | 128GB | 256GB | ||
| (Maximum Average Value) See Notes. | Idle: Reading: Writing: | 100 mA 255 mA 245 mA | 90mA 315mA 290mA | 110mA 450mA 390mA | 105mA 440mA 395mA | 105mA 475mA 585mA | 100mA 530mA 895mA |
NOTES: All values quoted are typical at ambient temperature and nominal supply voltage unless otherwise stated.
Sleep mode is specified under the condition that all drive inputs are static CMOS levels and in a “Not Busy“ operating state.
System Performance
All performance timings assume the drive controller is in the default (i.e., fastest) mode
Table 2-3. Performance
| 2242 | 2260/2280 | ||
| Read Transfer Rate | 8GB | Up to 140MBytes/sec | Up to 140MBytes/sec |
| 16GB | Up to 280MBytes/sec | Up to 280MBytes/sec | |
| 32GB | Up to 280MBytes/sec | Up to 550MBytes/sec | |
| 64GB | Up to 330MBytes/sec | Up to 550MBytes/sec | |
| 128GB | Up to 345MBytes/sec | Up to 560MBytes/sec | |
| 256GB | Up to 545MBytes/sec | Up to 560MBytes/sec | |
| Write Transfer Rate | 8GB | Up to 25 MBytes/sec | Up to 25MBytes/sec |
| 16GB | Up to 50 MBytes/sec | Up to 50MBytes/sec | |
| 32GB | Up to 45 MBytes/sec | Up to 100MBytes/sec | |
| 64GB | Up to 90 Mbytes/sec | Up to 90MBytes/sec | |
| 128GB | Up to 180 Mbytes/sec | Up to 185MBytes/sec | |
| 256GB | Up to 345 MBytes/sec | Up to 355MBytes/sec |
System Reliability
| Data Reliability | < 1 non-recoverable error in 1014 bits READ |
| Endurance (estimated TBW): 8GB 16GB 32GB 64GB 128GB 256GB | Up to 3TB/GB: 24TB 48TB 96TB 128TB 384TB 768TB |
Note: estimated TBW assumes workload consisting of mostly large block writes; TBW will be significantly reduced for workload consisting of mostly random small block writes.
Physical Specifications
The following sections provide the physical specifications for Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD products.
M.2 2260 SSD Physical Specifications
Cactus Technologies, Limited
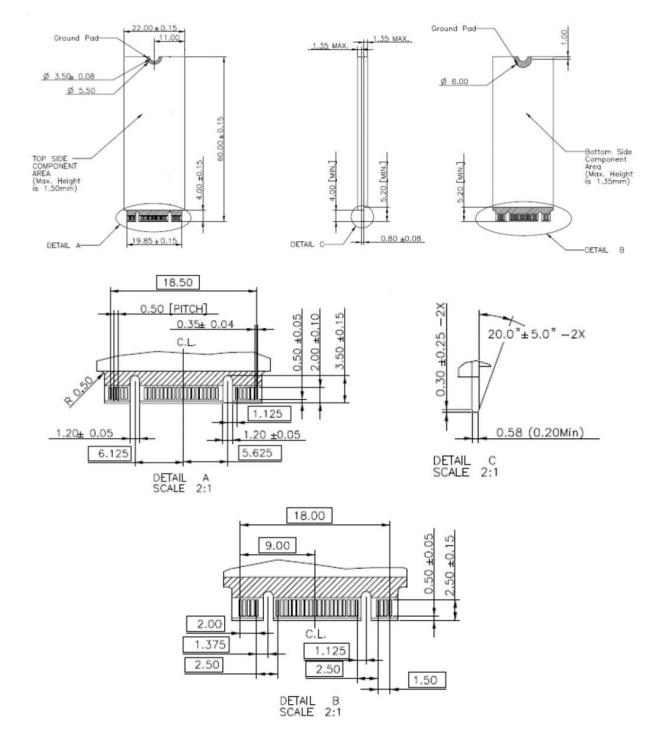
M.2 2280 SSD Physical Specifications
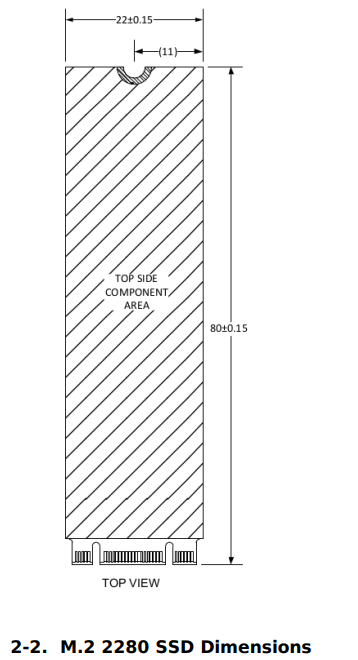
M.2 2242 SSD Physical Specifications
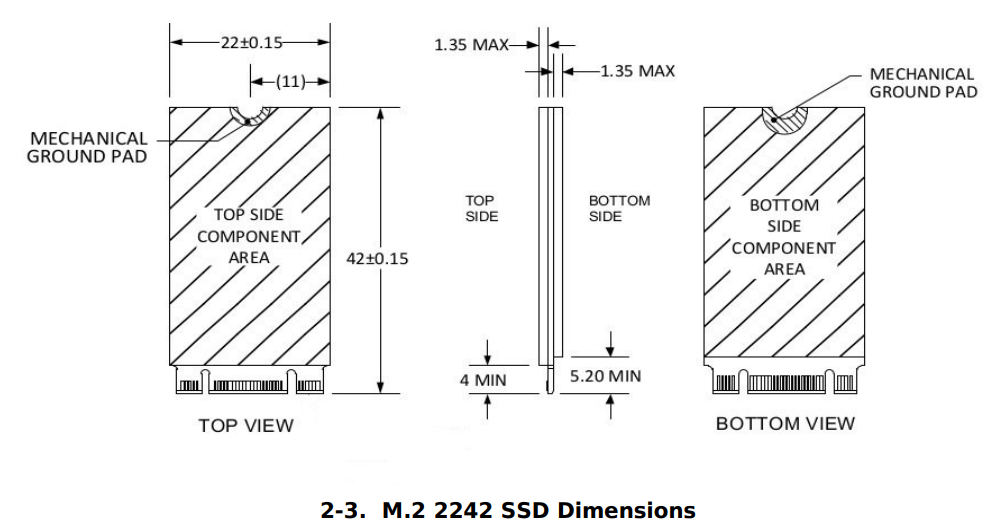
Note: key details and thickness measurements for 2242, 2260 and 2280 form factor are identical.
Capacities
Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD is available in 8, 16, 32, 64, 128 and 256GB capacities
Interface Description
The following sections provide detailed information on the Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC M.2 SSD interface.
M.2 SSD Pin Assignments and Pin Type
The signal/pin assignments and descriptions are listed in Table 3-5. 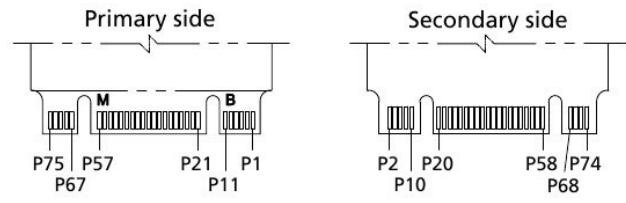
Table 3-5. M.2 SSD Pin Assignments and Pin Type
| Pin # | Pin Name | Description | Pin # | Pin Name | Description |
| 1 | CONFIG_3 | Connected to GND for SATA SSD | 2 | 3.3V | 3.3V supply |
| 3 | GND | 4 | 3.3V | ||
| 5 | N/C | No connect | 6 | Reserved | |
| 7 | DNU | 8 | Reserved | ||
| 9 | DNU | 10 | DAS/DSS | Drive activity | |
| 11 | N/C | No connect | 12 | B Key | |
| 13 | B Key | 14 | |||
| 15 | 16 | ||||
| 17 | 18 | ||||
| 19 | 20 | Reserved | |||
| 21 | CONFIG_0 | Connected to GND for SATA SSD | 22 | Reserved | |
| 23 | DNU | 24 | Reserved | ||
| 25 | DNU | 26 | Reserved | ||
| 27 | GND | 28 | Reserved | ||
| 29 | Reserved | 30 | Reserved | ||
| 31 | Reserved | 32 | Reserved | ||
| 33 | GND | 34 | Reserved | ||
| 35 | Reserved | 36 | Reserved | ||
| 37 | Reserved | 38 | DEVSLP | Device Sleep control; NO CONNECT 1 | |
| 39 | GND | 40 | Reserved | ||
| 41 | SATA RX+ | Host SATA receive differential pair | 42 | Reserved | |
| 43 | SATA RX- | 44 | Reserved | ||
| 45 | GND | 46 | Reserved | ||
| 47 | SATA TX- | Host SATA transmit differential pair | 48 | Reserved | |
| 49 | SATA TX+ | 50 | Reserved | ||
| Pin # | Pin Name | Description | Pin # | Pin Name | Description |
| 51 | GND | 52 | Reserved | ||
| 53 | Reserved | 54 | Reserved | ||
| 55 | Reserved | 56 | MFG_1 | Reserved for manufacturer use | |
| 57 | GND | 58 | MFG_2 | Reserved for manufacture use | |
| 59 | M Key | 60 | M Key | ||
| 61 | 62 | ||||
| 63 | 64 | ||||
| 65 | 66 | ||||
| 67 | DNU | 68 | SUSCLK | 32kHz clock input; not used | |
| 69 | CONFIG_1 | Connected to GND for SATA SSD | 70 | 3.3V | |
| 71 | GND | 72 | 3.3V | ||
| 73 | GND | 74 | 3.3V | ||
| 75 | CONFIG_2 | Connected to GND for SATA SSD |
Electrical Specifications
The following table defines all D.C. Characteristics for the M.2 SSD products. Unless otherwise stated, conditions are:
- Vcc = 3.3V ± 5%
- Ta = -40°C to 85°C
Absolute Maximum Ratings
| Parameter | Symbol | MIN | MAX | Unit s |
| Storage Temperature | Ts | -55 | +100 | oC |
| Operating Temperature | TA | -40 | +85 | oC |
| Vcc with respect to GND | Vcc | -0.3 | 3.6 | V |
DC Characteristics
| Parameter | Symbol | MIN | MAX | Unit s |
| Input Voltage | Vin | -0.5 | Vcc + 0.5 | V |
| Output Voltage | Vout | -0.3 | Vcc + 0.3 | V |
| Input Leakage Current | ILI | -10 | 10 | uA |
| Output Leakage Current | ILO | -10 | 10 | uA |
| Input/Output Capacitance | CI/Co | 10 | pF | |
| Operating Current Idle Active | ICC | 110 900 | mA |
AC Characteristics
Cactus Technologies® M.2 SSD products conforms to all AC timing requirements as specified in the Serial ATA v3.1 specifications. Please refer to that document for details of AC timing for all operation modes of the device
ATA Drive Register Set Definition and Protocol
The communication to or from the SSD is done using FIS. Legacy ATA protocol is supported by using the legacy mode defined in the SATA specifications. In this mode, the FIS has defined fields which provide all the necessary ATA task file registers for control and status information. The Serial ATA interface does not support Primary/Secondary or Master/Slave configurations. Each SATA channel supports only one SATA device, with the register selection as defined by the ATA standard.
ATA Task File Definitions
The following sections describes the usage of the ATA task file registers. Note that the Alternate Status Register of legacy ATA is not defined for SATA drives.
Data Register
The Data Register is a 16-bit register, and it is used to transfer data blocks between the SSD data buffer and the Host.
Error Register
This register contains additional information about the source of an error when an error is indicated in bit 0 of the Status register. The bits are defined as follows:
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | |
| BBK | UNC | 0 | IDNF | 0 | ABRT | 0 | AMNF | |
| Bit 7 (BBK) | This bit is set when a Bad Block is detected. | |||||||
| Bit 6 (UNC) | This bit is set when an Uncorrectable Error is encountered. | |||||||
| Bit 5 | This bit is 0. | |||||||
| Bit 4 (IDNF) | The requested sector ID is in error or cannot be found. | |||||||
| Bit 3 | This bit is 0. | |||||||
| Bit 2 (Abort) | This bit is set if the command has been aborted because of a status condition: (Not Ready, Write Fault, etc.) or when an invalid command has been issued. | |||||||
| Bit 1 This bit is 0. Bit 0 (AMNF) This bit is set in case of a general error. | ||||||||
| 6.1.3. Feature Register | ||||||||
Feature Register
This register provides information regarding features of the SSD that the host can utilize.
Sector Count Register
This register contains the number of sectors of data requested to be transferred on a read or write operation between the host and the SSD. If the value in this register is zero, a count of 256 sectors is specified. If the command was successful, this register is zero at command completion. If not successfully completed, the register contains the number of sectors that need to be transferred in order to complete the request.
Sector Number (LBA 7-0) Register
This register contains the starting sector number or bits 7-0 of the Logical Block Address (LBA) for any SSD data access for the subsequent command.
Cylinder Low (LBA 15-8) Register
This register contains the low order 8 bits of the starting cylinder address or bits 15-8 of the Logical Block Address
Drive/Head (LBA 27-24) Register
The Drive/Head register is used to select the drive and head. It is also used to select LBA addressing instead of cylinder/head/sector addressing. The bits are defined as follows:
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 | |||
| BUSY | RDY | DWF | DSC | DRQ | CORR | 0 | ERR | |||
| Bit 7 (BUSY) | The busy bit is set when the device has access to the command buffer and registers and the host is locked out from accessing the command register and buffer. No other bits in this register are valid when this bit is set to a 1. | |||||||||
| Bit 6 (RDY) | RDY indicates whether the device is capable of performing operations requested by the host. This bit is cleared at power up and remains cleared until the device is ready to accept a command. | |||||||||
| Bit 5 (DWF) | This bit, if set, indicates a write fault has occurred. | |||||||||
| Bit 4 (DSC) | This bit is set when the device is ready. | |||||||||
| Bit 3 (DRQ) | The Data Request is set when the device requires that information be transferred either to or from the host through the Data register. | |||||||||
| Bit 2 (CORR) | This bit is set when a Correctable data error has been encountered and the data has been corrected. This condition does not terminate a multi-sector read operation. | |||||||||
| Bit 1 (IDX) | This bit is always set to 0. | |||||||||
| Bit 0 (ERR) | This bit is set when the previous command has ended in some type of error. The bits in the Error register contain additional information describing the error. | |||||||||
| 6.1.10. | Device Control Register | |||||||||
Status Registers
These registers return the status when read by the host. Reading the Status register does clear a pending interrupt while reading the Auxiliary Status register does not. The meaning of the status bits are described as follows:
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| HOB | X | X | X | 1 | SW Rst | -IEn | 0 |
Bit 7 This bit is used in 48-bit addressing mode. When cleared, the host can read the most recently written values of the Sector Count,Drive/Head and LBA registers. When set, the host will read the previous written values of these registers. A write to any Command block register will clear this bit.
Bit 6 This bit is an X (Do not care).
Bit 5 This bit is an X (Do not care).
Bit 4 This bit is an X (Do not care).
Bit 3 This bit is ignored by the drive.
Bit 2 (SW Rst)This bit is set to 1 in order to force the drive to perform an AT Disk controller Soft Reset operation. The drive remains in Reset until this bit is reset to ‘0’.
Bit 1 (-IEn) The Interrupt Enable bit enables interrupts when the bit is 0. When the bit is 1, interrupts from the drive are disabled. This bit is set to 0 at power on and Reset.
Bit 0 This bit is ignored by the drive.
Device Control Register
This register is used to control the drive interrupt request and to issue an ATA soft reset to the drive. The bits are defined as follows:
| D7 | D6 | D5 | D4 | D3 | D2 | D1 | D0 |
| X | -WTG | -HS3 | -HS2 | -HS1 | -HS0 | -nDS1 | -nDS0 |
Bit 7 This bit is unknown.
Implementation Note:
Conflicts may occur on the host data bus when this bit is provided by a Floppy Disk Controller operating at the same addresses as the SSD. Following are some possible solutions to this problem:
- Locate the SSD at a non-conflicting address (i.e., Secondary address (377) when a Floppy Disk Controller is located at the Primary addresses).
- Do not install a Floppy and a SSD in the system at the same time.
- Implement a socket adapter that can be programmed to (conditionally) tri-state D7 of I/0 address 3F7/377 when a SSD product is installed and conversely to tri-state D6-D0 of I/O address 3F7/377 when a floppy controller is installed.
- Do not use the SSD’s Drive Address register. This may be accomplished by either a) If possible, program the host adapter to enable only I/O addresses 1F0-1F7, 3F6 (or 170-
177, 176) to the SSD or b) if provided use an additional Primary/Secondary configuration in the SSD that does not respond to accesses to I/O locations 3F7 and 377. With either of these implementations, the host software must not attempt to use information in the Drive Address Register.
| Bit 6 (-WTG) | This bit is 0 when a write operation is in progress, otherwise, it is 1. |
| Bit 5 (-HS3) | This bit is the negation of bit 3 in the Drive/Head register. |
| Bit 4 (-HS2) | This bit is the negation of bit 2 in the Drive/Head register. |
Bit 3 (-HS1) This bit is the negation of bit 1 in the Drive/Head register.
Bit 2 (-HS0) This bit is the negation of bit 0 in the Drive/Head register.
Bit 1 (-nDS1) This bit is 0 when drive 1 is active and selected.
Bit 0 (-nDS0) This bit is 0 when the drive 0 is active and selected.
Drive Address Register
This register is provided for compatibility with the AT disk drive interface. It is recommended that this register not be mapped into the host’s I/O space because of potential conflicts on Bit 7. The bits are defined as follows:
| X | -WTG | -HS3 | -HS2 | -HS1 | -HS0 | -nDS1 | -nDS0 |
Bit 7 This bit is unknown.
Implementation Note:
Conflicts may occur on the host data bus when this bit is provided by a Floppy Disk Controller operating at the same addresses as the SSD. Following are some possible solutions to this problem:
- Locate the SSD at a non-conflicting address (i.e., Secondary address (377) when a Floppy Disk Controller is located at the Primary addresses).
- Do not install a Floppy and a SSD in the system at the same time.
- Implement a socket adapter that can be programmed to (conditionally) tri-state D7 of I/0 address 3F7/377 when a SSD product is installed and conversely to tri-state D6-D0 of I/O address 3F7/377 when a floppy controller is installed.
- Do not use the SSD’s Drive Address register. This may be CACTUS MLC-240S Industrial Series M.2 SSD accomplished by either a) If possible, program the host adapter to enable only I/O addresses 1F0-1F7, 3F6 (or 170-
177, 176) to the SSD or b) if provided use an additional Primary/Secondary configuration in the SSD that does not respond to accesses to I/O locations 3F7 and 377. With either of these implementations, the host software must not attempt to use information in the Drive Address Register.
| Bit 6 (-WTG) | This bit is 0 when a write operation is in progress, otherwise, it is 1. |
| Bit 5 (-HS3) | This bit is the negation of bit 3 in the Drive/Head register. |
| Bit 4 (-HS2) | This bit is the negation of bit 2 in the Drive/Head register. |
Bit 3 (-HS1) This bit is the negation of bit 1 in the Drive/Head register.
Bit 2 (-HS0) This bit is the negation of bit 0 in the Drive/Head register.
Bit 1 (-nDS1) This bit is 0 when drive 1 is active and selected.
Bit 0 (-nDS0) This bit is 0 when the drive 0 is active and selected.
ATA Command Description
This section defines the ATA command set supported by Cactus Technologies® M.2 SSDs.
ATA Command Set
Table 5-6 summarizes the supported ATA command set .
| COMMAND | Code |
| Check Power Mode | E5h, 98h |
| Data Set Management | 06h |
| Execute Drive Diagnostic | 90h |
| Flush Cache | E7h |
| Flush Cache Ext | EAh |
| Identify Drive | ECh |
| Idle | E3h, 97h |
| Idle Immediate | E1h, 95h |
| Initialize Drive Parameters | 91h |
| NOP | 00h |
| Read Buffer | E4h |
| Read DMA | C8h |
| Read DMA Ext | 25h |
| Read FPDMA Queued | 60h |
| Read Multiple | C4h |
| Read Multiple Ext | 29h |
| Read Sector(s) | 20h, 21h |
| Read Sector(s) Ext | 24h |
| Read Verify Sector(s) | 40h, 41h |
| Read Verify Sector(s) Ext | 42h |
| Security Disable Password | F6h |
| Security Erase Prepare | F3h |
| Security Erase Unit | F4h |
| Security Freeze Lock | F5h |
| Security Set Password | F1h |
| Security Unlock | F2h |
| Seek | 70h |
| Set Features | EFh |
| Set Multiple Mode | C6h |
| Set Sleep Mode | E6h, 99h |
| SMART | B0h |
| Stand By | E2h, 96h |
| Stand By Immediate | E0h, 94h |
| COMMAND | Code |
| Write Buffer | E8h |
| Write DMA | CAh |
| Write DMA Ext | 35h |
| Write FPDMA Queued | 61h |
| Write Multiple | C5h |
| Write Multiple Ext | 39h |
| Write Sector(s) | 30h, 31h |
| Write Sector(s) Ext | 34h |
S.M.A.R.T. Feature Set
Cactus Technologies® -240 Series M.2 SSD supports S.M.A.R.T. CACTUS MLC-240S Industrial Series M.2 SSD attribute reporting. This following subcommands are supported when programmed into the Feature Register:
| Value | Command | Value | Command |
| D0h | Read Data | D5h | Reserved |
| D1h | Read Attribute Threshold | D6h | Reserved |
| D2h | Enable/Disable Autosave | D8h | Enable SMART operationes |
| D3h | Save Attribute Values | D9h | Disable SMART operations |
| D4h | Execute OFF-LINE Immediate | DAh | Return Status |
S.M.A.R.T Data Structure
The Read Data commands returns 512 bytes of data in the following structure:
| Byte | Description |
| 0-1 | Revision code |
| 2-361 | Vendor specific |
| 362 | Off-line data collection status |
| 363 | Self-test execution status byte |
| 364-365 | Total time in seconds to complete off-line data collection activitiies |
| 366 | Vendor specific |
| 367 | Off-line data collection capabilities |
| 368-369 | SMART capabilities |
| 370 | Error logging capabilities: bit[7:1] – reserved; bit[0]: 1=device error logging supported |
| 371 | Vendor specific |
| 372 | Short self-test routine recommended polling time (in minutes) |
| Byte | Description |
| 373 | Extended self-test routine recommended polling time (in minutes) |
| 374 | Conveyance self-test routine recommended polling time (in minutes) |
| 375-385 | Reserved |
| 386-395 | Firmware Version/Date Code |
| 396-397 | Reserved |
| 398-399 | Reserved |
| 400-405 | ‘SM2246’ |
| 406-510 | Vendor specific |
| 511 | Data structure checksum |
S.M.A.R.T Attributes
The following table lists the attributes returned in bytes 2-36 CACTUS MLC-240S Industrial Series M.2 SSD of the 512-byte SMART data.Byte 0 is Attribute ID, bytes 1-2 are status flags, bytes 3-4 are reserved bytes; the table below shows the definition for bytes 5-11:
| Attribute ID | Attribute values | Attribute Name | ||||||
| Byte 5 | Byte 6 | Byte 7 | Byte 8 | Byte 9 | Byte 10 | Byte 11 | ||
| 01h | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | Read error rate |
| 05h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | Reallocated sectors count |
| 09h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | Power on hours | ||
| 0Ch | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | Power cycle count | ||
| A0h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | Uncorrectable sector count when read/write | |||
| A1h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | Number of valid spare block |
| A3h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | 00 | Number of initial invalid block |
| A4h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | Total erase count | ||
| A5h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | Max. Erase count | ||
| A6h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | Min. Erase count | ||
| A7h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | Average erase count | ||
| A8h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | Max. erase count spec. | ||
| A9h | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | Percent remaining life | ||
| AFh | LSB | MSB | 00 | 00 | 00 | Program fail count in worse die | ||
Appendix A. Ordering Information
Model KDXFI-240SZ
Where: X is drive capacities: 8G —————- 8GB
16G ————– 16GB
32G ————– 32GB 64G ————– 64GB
128G ———— 128GB
256G ———— 256GB
Where: I is temperature grade:
blank ———— standard
I ——————- extended
Where: Z is form factor:
M5 —————- 2260
M6 —————- 2242
M7 —————- 2280 (64/128/256G only)
Example:
- 8GB M.2 2260 SSD ———————————————————– KD8GF-240SM5
- 8GB M.2 SSD 2260 extended temp. ———————————— KD8GFI-240SM5
- 256GB M.2 2242 SSD ——————————————————- KD256GF-240SM6
- 64GB M.2 2280 SSD ——————————————————— KD64GF-240SM7
Appendix B.Technical Support Services
B.1.Direct Cactus Technologies® Technical Support
Email: tech@cactus-tech.com
Appendix C.Cactus Technologies® Worldwide Sales Offices
Email: sales@cactus-tech.com
Email: americas@cactus-tech.com
Appendix D.Limited Warranty
- WARRANTY STATEMENT
Cactus Technologies® warrants its Industrial MLC Grade products only to be free of any defects in materials or workmanship that would prevent them from functioning properly for two years from the date of purchase or when rated TBW is exceeded, whichever CACTUS MLC-240S Industrial Series M.2 SSD occurs first. This express warranty is extended by Cactus Technologies® Limited to customers of our products. - GENERAL PROVISIONS
This warranty sets forth the full extent of Cactus Technologies® responsibilities regarding the Cactus Technologies® Industrial MLC Grade Flash Storage Products. Cactus Technologies®, at its sole option, will repair, replace or refund the purchase price of the defective product. Cactus Technologies® guarantees our products meet all specifications detailed in our CACTUS MLC-240S Industrial Series M.2 SSD product manuals. Although Cactus Technologies® products are designed to withstand harsh environments and have the highest specifications in the industry, they are not warranted to never have failure and Cactus Technologies® does not warranty against incidental or consequential damages. Accordingly, in any use of products in life support systems or other applications where failure could cause injury or loss of life, the products should only be incorporated in systems designed with appropriate redundancy, fault tolerant or backup features. - WHAT THIS WARRANTY COVERS
For products found to be defective, Cactus Technologies® will have the option of repairing, replacing or refunding the purchase price the defective product, if the following conditions are met:
A. The defective product is returned to Cactus Technologies® for failure analysis as soon as possible after the failure occurs.
B. An incident card filled out by the user, explaining CACTUS MLC-240S Industrial Series M.2 SSD the conditions of usage and the nature of the failure, accompanies each returned defective product.
C. No evidence is found of abuse or operation of products not in accordance with the published specifications, or of exceeding maximum ratings or operating conditions.
All failing products returned to Cactus Technologies® under the provisions of this limited warranty shall be tested to the product’s functional and performance specifications. Upon confirmation of failure, each product will be analyzed, by whatever means necessary, to determine the root cause of failure. If the root cause of failure is found to be not covered by the above provisions, then the product will be returned to the customer with a report indicating why the failure was not covered under the warranty.
This warranty does not cover defects, malfunctions, performance failures or damages to the unit resulting from use in other than its normal and customary manner, misuse, accident or neglect; or improper alterations or repairs. Cactus Technologies® Limited may repair or replace, at its discretion, any product returned by its customers, even if CACTUS MLC-240S Industrial Series M.2 SSD such product is not covered under warranty, but is under no obligation to do so. - RECEIVING WARRANTY SERVICE
According to Cactus Technologies® warranty procedure, defective product should be returned only with prior authorization from Cactus Technologies® Limited. Please contact Cactus Technologies® Customer Service department (tech@cactus-tech.com) with the following information: product model number and description, nature of defect, conditions of use, proof of purchase and purchase date. If approved, Cactus Technologies® will issue a Return Material Authorization or Product Repair Authorization number with shipping instructions.
FAQs
What is the CACTUS MLC-240S SSD designed for?
A tough industrial-grade M.2 SATA III SSD designed for use in severe environments, embedded systems, and mission-critical applications is the MLC-240S. When using MLC (Multi-Level Cell) NAND flash, it offers excellent durability, dependability, and long-term product availability.
What form factor is this SSD?
The MLC-240S comes in the M.2 2242 or 2280 form factors, which measure 42 or 80 mm in length and 22 mm in width. Make sure your host device can accommodate the appropriate size at all times.
What interface does the MLC-240S use?
Instead of NVMe, it employs a SATA III (6Gbps) interface. This indicates that M.2 B-key or B+M-key slots made for SATA SSDs can use it.
What is MLC NAND and why is it used in this drive?
MLC (Multi-Level Cell) NAND provides a balance between capacity and endurance by storing two bits per cell. It is perfect for industrial use cases that require dependable performance under repeated write operations because it is less costly than SLC and more robust than TLC.
Can it operate in extreme temperatures?
Indeed. The MLC-240S series is appropriate for industrial PCs, outdoor systems, and automotive settings due to its broad operating temperature range, which is normally between -40°C and +85°C.
Does this SSD support power loss protection?
Power Loss Protection (PLP) is a feature of some MLC-240S models that safeguards in-flight data in the event of unplanned power failures. To be sure, consult the datasheet for your model.
What capacities are available for this SSD?
Generally, the MLC-240S is available in sizes between 16GB to 512GB, contingent on the product configuration and form factor.
What are the endurance and write cycle expectations?
The drive is rated for greater endurance than consumer SSDs because to MLC NAND and industrial firmware optimisations; depending on workload and capacity, it may frequently withstand up to 3,000 to 10,000 program/erase (P/E) cycles per block.



